In a historic milestone for India’s medical innovation and biotechnology sector, Prime Minister Narendra Modi today launched NexCAR19, the nation’s first indigenously developed CAR T-cell therapy, marking a monumental leap in the country’s cancer treatment capabilities. Developed under the Make in India initiative, this cutting-edge therapy represents a transformative stride in precision medicine — offering new hope to thousands of cancer patients.
A Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment
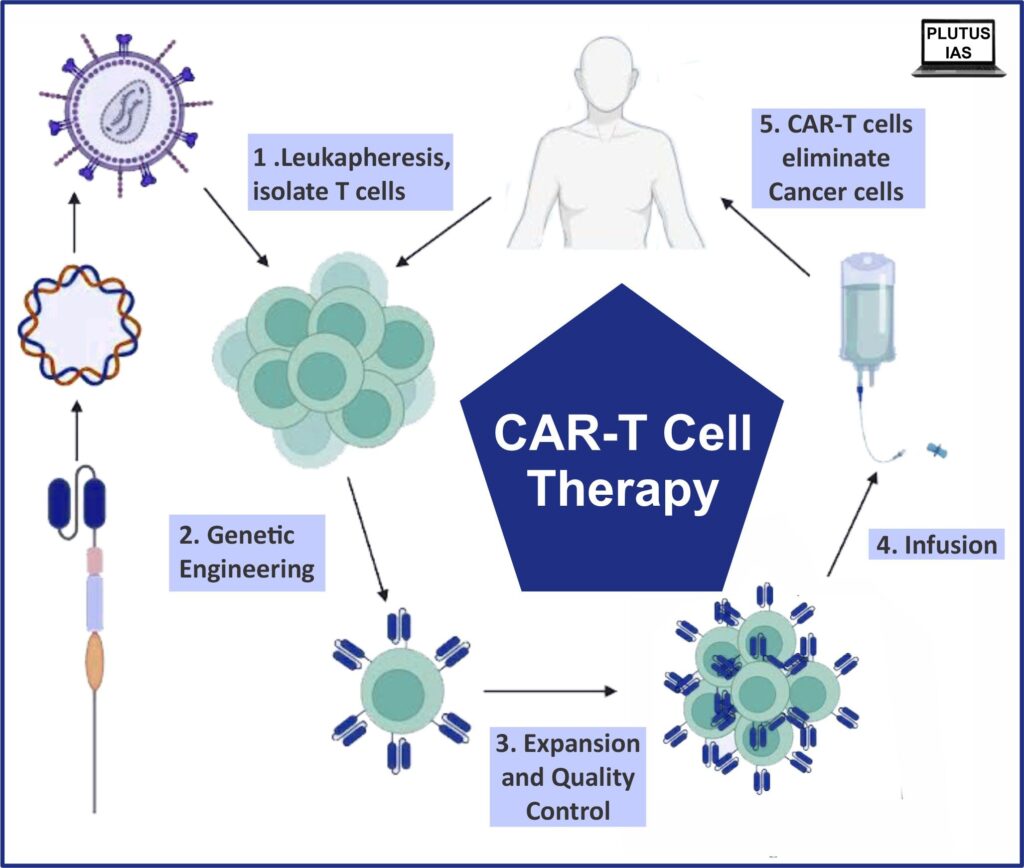
CAR T-cell therapy, short for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy, is a revolutionary immunotherapy where a patient’s own immune cells are genetically engineered to fight cancer cells. NexCAR19, developed by ImmunityBio India in collaboration with Tata Memorial Centre and supported by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), is the first of its kind to be designed, tested, and manufactured entirely in India.
Until now, CAR T-cell treatments were available only in the US and Europe, costing upwards of ₹3–4 crore — far beyond the reach of most Indian patients. NexCAR19 changes that narrative, bringing affordable and accessible cancer care within India’s borders, at an estimated cost that is 70–80% lower than international therapies.
The Prime Minister’s Vision: India Leading in Bio-innovation
Speaking at the launch event in New Delhi, Prime Minister Modi hailed the innovation as a symbol of India’s growing self-reliance in healthcare technology.
“NexCAR19 is not just a medical breakthrough — it’s a testament to India’s innovation ecosystem and our commitment to make cutting-edge healthcare affordable to all,” said PM Modi.
He also emphasized that the Atmanirbhar Bharat mission in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals has begun yielding tangible results, placing India on the global map as a center for medical research and innovation.
What Makes NexCAR19 Unique
Unlike conventional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation, NexCAR19 directly targets cancer cells by using the patient’s immune system as a precision weapon. Here’s how it works:
- T-Cell Collection: A sample of the patient’s white blood cells is extracted.
- Genetic Engineering: Scientists modify these T-cells in the lab to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that recognizes specific proteins on cancer cells.
- Cell Expansion: The engineered T-cells are multiplied in controlled lab environments.
- Infusion: The modified T-cells are reintroduced into the patient’s body, where they identify and destroy cancer cells.
The therapy is especially effective for patients with leukemia and lymphoma, where traditional treatments often fall short. Early clinical trials of NexCAR19 have shown remarkable remission rates, with minimal side effects and quicker recovery.
Collaboration Behind the Innovation
The journey of NexCAR19 began as a collaborative research initiative between the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT-B), Tata Memorial Centre (TMC), and ImmunityBio India (a joint venture with US-based ImmunoACT). With regulatory support from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) and funding from the Department of Biotechnology, the therapy has now reached commercial readiness.
Dr. (Prof.) G.K. Rath, senior oncologist at Tata Memorial, noted:
“This is not merely an import of technology — it’s a true Indian innovation built from research, clinical validation, and patient care experience over several years.”
Transforming India’s Oncology Landscape
With over 14 lakh new cancer cases reported annually in India, the introduction of NexCAR19 could be a turning point in treatment outcomes. Currently, most advanced therapies are either unavailable or unaffordable for Indian patients. NexCAR19’s local production means that hospitals across the country — starting with AIIMS, Tata Memorial, and major regional cancer centers — will soon be equipped to offer this therapy.
Experts predict that India could soon become a global hub for affordable cell and gene therapies, exporting innovation to developing countries facing similar healthcare challenges.
Economic and Healthcare Implications
The rollout of NexCAR19 aligns perfectly with India’s dual focus on healthcare access and biotech manufacturing growth. The therapy’s development and production are expected to:
- Create hundreds of skilled biotech jobs across labs and hospitals.
- Boost India’s R&D exports in pharmaceutical technology.
- Reduce dependence on foreign cancer drug imports, saving millions in healthcare expenditure.
Industry analysts estimate that India’s biotech economy, currently valued at around $150 billion, could grow by another 20% annually with innovations like NexCAR19 leading the charge.
Affordable Innovation for All
One of the biggest highlights of NexCAR19 is its cost-effectiveness. While imported CAR T-cell therapies in the West cost between ₹3 to ₹4 crore, the Indian-developed NexCAR19 is expected to be priced at approximately ₹30–40 lakh, making it nearly 10 times cheaper.
For families battling blood cancers, this brings a renewed sense of hope — not just in terms of treatment efficacy, but financial feasibility as well.
The Road Ahead: Expanding Research and Accessibility
Following the successful clinical trials, the Government of India and the Department of Biotechnology plan to expand CAR T-cell therapy research into solid tumors such as breast, lung, and brain cancers. The next phase includes setting up CAR T-cell labs and manufacturing facilities in multiple states to decentralize access.
AIIMS New Delhi, Tata Memorial Mumbai, and CMC Vellore are expected to be among the first institutions offering NexCAR19 treatment on a larger scale by early 2026.
Furthermore, discussions are underway to include NexCAR19 under government health schemes like Ayushman Bharat, potentially providing financial coverage to underprivileged patients.
Global Recognition for Indian Science
The international medical community has lauded India’s achievement. Leading oncologists from the US and Europe have praised the country’s rapid progress in gene therapy technology, especially considering that CAR T-cell therapy has taken years to commercialize even in developed markets.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) have also recognized India’s contribution to democratizing advanced cancer care.
From Lab to Life: A New Era Begins
The launch of NexCAR19 marks more than just a scientific success — it’s a symbol of how public-private partnerships, government support, and academic research can converge to solve humanity’s most pressing health challenges.
With India now entering the global stage of next-generation therapeutics, the country stands poised to lead the future of affordable medical innovation, not just for cancer, but for a wide range of chronic diseases.
Key Takeaways
- NexCAR19 is India’s first homegrown CAR T-cell therapy, developed indigenously under the Make in India mission.
- The therapy offers personalized cancer treatment at nearly one-tenth the global cost.
- Collaboration between IIT Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and ImmunityBio India made this breakthrough possible.
- The initiative reflects India’s growing self-reliance in biotechnology and healthcare innovation.
- NexCAR19 could pave the way for India to become a global hub for affordable advanced therapies.
Conclusion
The launch of NexCAR19 is a defining moment in India’s healthcare journey — a moment where innovation meets compassion. It proves that with determination, collaboration, and vision, India can not only treat its own people but lead the world in medical breakthroughs.
As Prime Minister Modi aptly put it, “When India innovates, the world benefits.”

