In a significant step toward strengthening South–South cooperation, India and Namibia have agreed to deepen cooperation in defense and critical minerals, marking a new phase in their strategic partnership. The agreement reflects evolving global realities where security, supply chains, and access to critical resources are becoming central to international relations.
The enhanced cooperation underscores shared interests in regional stability, sustainable development, and economic resilience, while also highlighting Africa’s growing importance in India’s long-term strategic and industrial planning.
A New Chapter in India–Namibia Relations
India and Namibia share a relationship rooted in:
- Historical solidarity
- Support during Namibia’s independence movement
- Shared commitment to multilateralism and the Global South
Over the years, bilateral ties have expanded across diplomacy, trade, capacity building, and development cooperation. The latest agreement to deepen defense and critical minerals cooperation elevates this relationship into a strategic domain.
Why This Agreement Matters Today
The global environment has changed dramatically in recent years due to:
- Geopolitical tensions
- Supply chain disruptions
- Energy transition requirements
- Growing competition over strategic resources
In this context, partnerships like the India–Namibia agreement are not just bilateral—they are strategic responses to global uncertainty.
Defense Cooperation: Strengthening Security Partnerships
Expanding Defense Engagement
The agreement envisions closer cooperation in:
- Defense training and capacity building
- Military exchanges and joint exercises
- Knowledge sharing in peacekeeping operations
- Maritime and regional security
India has extensive experience in:
- UN peacekeeping
- Military training institutions
- Defense technology and logistics
Namibia, which values professional military development and regional stability, sees India as a trusted and non-intrusive defense partner.
Defense Diplomacy and the Global South
India’s defense cooperation model emphasizes:
- Mutual respect
- Capacity building rather than dependency
- Long-term institutional partnerships
For Namibia, this aligns with its vision of maintaining sovereignty while enhancing defense preparedness.
For India, deeper defense ties in southern Africa strengthen:
- Its presence in the Indian Ocean–Africa security continuum
- Cooperation with like-minded nations
- Its role as a net security provider
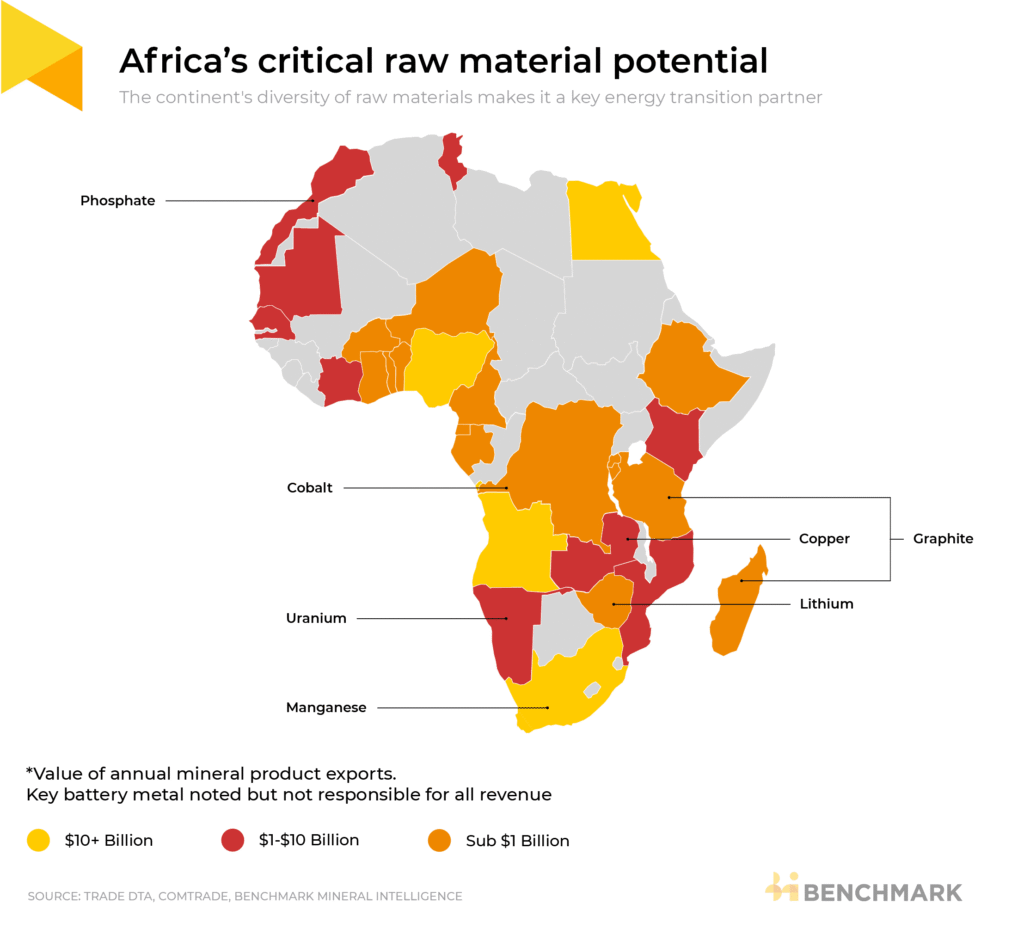
Critical Minerals: A Strategic Imperative
What Are Critical Minerals?
Critical minerals include resources essential for:
- Renewable energy technologies
- Electric vehicles
- Battery storage
- Electronics and semiconductors
- Defense and aerospace systems
These include lithium, cobalt, rare earth elements, graphite, and other strategic minerals.
Namibia’s Mineral Wealth
Namibia is rich in mineral resources and has emerged as an important player in:
- Uranium production
- Lithium and rare earth exploration
- Sustainable mining practices
Its stable political environment and transparent mining framework make it an attractive partner for long-term mineral cooperation.
Why India Needs Critical Minerals
India’s ambitions in:
- Clean energy transition
- Electric mobility
- Advanced manufacturing
- Defense self-reliance
depend heavily on secure access to critical minerals.
Currently, global supply chains for these minerals are:
- Highly concentrated
- Vulnerable to geopolitical risks
By partnering with Namibia, India aims to:
- Diversify sources
- Reduce supply chain risks
- Secure long-term access to strategic inputs
A Win–Win Partnership Model
Beyond Extraction
The India–Namibia cooperation is not limited to raw material extraction. It emphasizes:
- Value addition
- Skill development
- Technology transfer
- Sustainable and responsible mining
This ensures that Namibia benefits through:
- Local employment
- Industrial development
- Capacity building
while India gains secure and ethical access to resources.
Sustainability and Responsible Mining
Both countries have emphasized:
- Environmentally responsible mining
- Community participation
- Long-term ecological balance
This aligns with global standards on:
- ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) practices
- Sustainable development goals
Such an approach differentiates this partnership from exploitative models often criticized in resource-rich regions.
Strategic Importance for Africa–India Relations
Africa in India’s Global Strategy
Africa plays a central role in India’s:
- Global South diplomacy
- Energy and resource security
- Trade and investment expansion
Namibia’s role as a stable, resource-rich, and strategically located country makes it a valuable partner.
Strengthening South–South Cooperation
The agreement reinforces:
- South–South partnerships
- Shared development models
- Mutual growth without political conditionalities
It reflects India’s approach of development partnership rather than donor–recipient relationships.
Economic and Industrial Impact
For India
The cooperation supports:
- Manufacturing under clean energy initiatives
- Electric vehicle supply chains
- Defense production and innovation
- Reduced import dependence
Secure mineral access is critical for sustaining industrial growth.
For Namibia
Namibia stands to gain through:
- Increased foreign investment
- Technology and expertise sharing
- Job creation in mining and downstream industries
- Enhanced global market integration
This partnership supports Namibia’s goal of moving up the value chain.
Defense and Minerals: A Strategic Convergence
The coupling of defense and critical minerals cooperation is significant because:
- Modern defense systems rely heavily on advanced materials
- Energy security and national security are increasingly linked
- Strategic autonomy requires control over both technology and resources
India and Namibia recognize this convergence and are aligning their cooperation accordingly.
Multilateral and Global Implications
The agreement also has wider implications:
- It supports global supply chain diversification
- Reduces overdependence on limited suppliers
- Promotes stability through economic interdependence
It also strengthens cooperation among democracies and developing nations in shaping a more balanced global order.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite strong potential, challenges remain:
- Infrastructure development in mining regions
- Regulatory coordination
- Global price volatility of minerals
- Need for long-term investment commitments
Addressing these will require:
- Continuous diplomatic engagement
- Private sector participation
- Policy alignment
Long-Term Vision of the Partnership
The India–Namibia agreement is not a short-term arrangement. It signals:
- Long-term strategic trust
- Shared vision for sustainable development
- Commitment to resilience and autonomy
Future cooperation could expand into:
- Renewable energy projects
- Green hydrogen
- Advanced materials research
- Skill and academic exchange
A Model for Future Partnerships
This cooperation could serve as a model for:
- India’s engagement with other African nations
- Ethical resource partnerships
- Balanced defense diplomacy
It demonstrates how countries can collaborate strategically without compromising sovereignty or sustainability.
Conclusion
The agreement between India and Namibia to deepen cooperation in defense and critical minerals marks a major milestone in their bilateral relations. It reflects a shared understanding of modern strategic challenges—where security, resources, and sustainability are deeply interconnected.
For India, the partnership strengthens energy security, industrial growth, and strategic autonomy.
For Namibia, it offers responsible investment, capacity building, and economic diversification.
More broadly, this cooperation reinforces the idea that the future of global partnerships lies in trust-based, sustainable, and mutually beneficial engagement. As India and Namibia move forward together, their collaboration stands as a strong example of how Global South nations can shape resilient and equitable strategic partnerships in an increasingly complex world.

