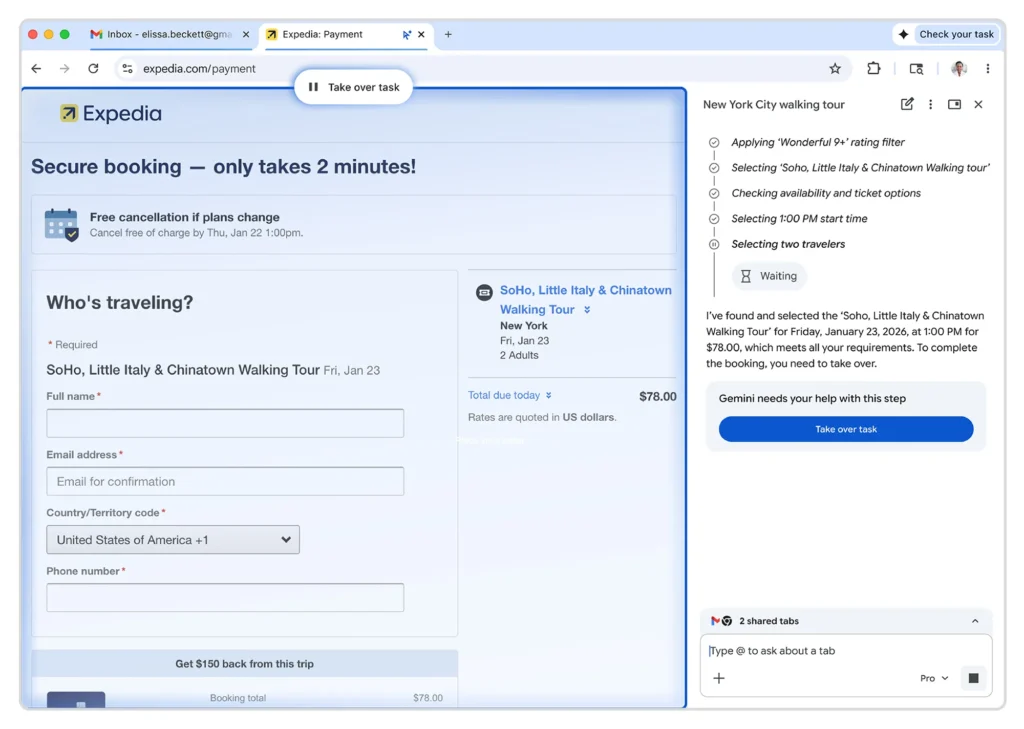
n a major step toward redefining how people interact with the internet, Google has announced that its AI agent can now browse the web on users’ behalf, completing tasks that previously required manual searching, clicking, and form-filling. The development marks a significant evolution in artificial intelligence—from systems that merely answer questions to agents that can act independently in digital environments.
This announcement signals the arrival of a new phase in the internet era, where AI doesn’t just assist users but actively performs online actions, potentially transforming productivity, search behavior, and the future of human–computer interaction.
What Does “AI Agent Browsing on Behalf of Users” Mean?
Traditionally, AI tools helped users by:
- Summarizing information
- Answering queries
- Recommending content
Google’s new AI agent goes a step further. It can:
- Navigate websites autonomously
- Click links and buttons
- Fill forms based on instructions
- Compare information across multiple pages
- Complete multi-step online tasks
In simple terms, the AI agent behaves like a virtual user, carrying out browser-based actions under user direction.
From Search Engine to Digital Agent
Google built its dominance on search—helping users find information. This new AI agent shifts the paradigm from search to execution.
Instead of:
“Here are the links you asked for.”
The AI can now say:
“I found the information, compared options, and completed the task for you.”
This transition positions Google not just as a gateway to information, but as an active digital operator.
Key Capabilities of Google’s AI Browsing Agent
1. Autonomous Web Navigation
The AI agent can move through websites much like a human:
- Opening pages
- Scrolling content
- Selecting relevant links
It understands page structure and adapts to different layouts, even on unfamiliar sites.
2. Task-Oriented Browsing
Users can give high-level instructions such as:
- “Find the cheapest flight for this route”
- “Compare insurance plans and summarize differences”
- “Book a table at a restaurant”
The agent then breaks the request into steps and completes them online.
3. Multi-Site Comparison
Unlike traditional search, the AI agent can:
- Visit multiple websites
- Extract key data
- Compare prices, features, or policies
- Present a consolidated result
This saves time and reduces cognitive overload for users.
4. Form Filling and Interaction
The agent can:
- Enter information into forms
- Select dropdown options
- Navigate checkout or booking flows
All actions are performed with user awareness and permission.
How This Changes the User Experience
Less Clicking, More Results
Users no longer need to:
- Open dozens of tabs
- Read through repetitive pages
- Manually compare options
The AI handles the heavy lifting while users focus on decisions.
Productivity Boost
For professionals and everyday users alike, the AI agent can:
- Automate repetitive online tasks
- Speed up research
- Reduce time spent on routine browsing
This could fundamentally change workflows across industries.
Why Google Is Making This Move Now
The Rise of AI Agents
The AI industry is shifting from chat-based tools to agentic systems—AI that can:
- Plan tasks
- Make decisions
- Take actions
Google’s browsing agent reflects this broader trend.
Competition in the AI Space
With multiple tech giants investing heavily in AI, Google’s move signals:
- A push to maintain leadership in web interaction
- A strategy to keep users within its ecosystem
- An evolution beyond traditional search
AI agents represent the next competitive frontier.
Privacy, Control, and User Trust
User Consent Is Central
Google has emphasized that:
- The AI agent acts only on user instruction
- Users can monitor and stop actions at any time
- Sensitive tasks require explicit confirmation
This aims to ensure trust and transparency.
Data Security Considerations
Browsing on a user’s behalf raises important questions:
- How is personal data handled?
- What information is stored?
- How are credentials protected?
Google states that strong security and privacy safeguards are built into the system.
Implications for the Future of Search
From Queries to Outcomes
Search may evolve from:
- Keyword-based queries
to - Goal-based instructions
Instead of asking what, users will increasingly ask do.
Impact on Websites and Businesses
If AI agents become common:
- Websites may see fewer direct human visitors
- Content may need to be optimized for AI readability
- User experience design could shift toward agent-friendly interfaces
This could reshape digital marketing and SEO strategies.
Potential Use Cases Across Sectors
E-commerce
AI agents can:
- Compare products
- Track price drops
- Complete purchases
This could redefine online shopping.
Travel and Hospitality
Agents can:
- Plan trips
- Book tickets and hotels
- Manage itineraries
Reducing planning time dramatically.
Finance and Services
AI agents could:
- Compare financial products
- Fill applications
- Track deadlines and renewals
While maintaining user oversight.
Education and Research
Students and researchers can:
- Gather sources
- Compare studies
- Summarize findings
All through agent-driven browsing.
Ethical and Regulatory Questions
Accountability
If an AI agent makes a mistake:
- Who is responsible?
- The user, the platform, or the AI system?
These questions will shape future regulation.
Fair Competition
Automated browsing could:
- Give larger platforms an advantage
- Change traffic patterns across the web
Regulators may closely watch how such agents affect digital ecosystems.
How This Fits Into Google’s Long-Term Vision
Google’s AI browsing agent aligns with its broader goal of:
- Making AI a universal assistant
- Embedding intelligence across products
- Reducing friction between intent and action
It represents a shift toward ambient computing, where technology works quietly in the background.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its promise, the technology faces hurdles:
- Complex website structures
- Constantly changing web layouts
- Anti-bot protections
- Ensuring reliability at scale
Overcoming these will determine how quickly AI agents become mainstream.
What This Means for Users
For users, this development offers:
- More convenience
- Less digital fatigue
- Faster access to outcomes
But it also requires:
- New digital literacy
- Understanding AI limitations
- Active oversight of automated actions
A Turning Point for the Internet
Google’s announcement suggests the internet is entering a new phase:
- From browsing to delegation
- From searching to execution
- From tools to autonomous assistants
The way humans interact with the web may never be the same again.
Conclusion
Google’s announcement that its AI agent can now browse on users’ behalf marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of artificial intelligence and the internet itself. By enabling AI to navigate websites, compare information, and complete tasks, Google is transforming AI from a passive assistant into an active digital agent.
While challenges around privacy, trust, and regulation remain, the potential benefits—time savings, efficiency, and reduced complexity—are immense. As AI agents become more capable, the internet may shift from a place users explore manually to an environment where goals are stated and outcomes are delivered.
This development is not just a feature update—it is a glimpse into the future of how humans and AI will collaborate online.